In the V century. BC, Leuccipus said there was only one type of matter and thought that if we divided the matter into ever smaller parts, we get a piece that could not cut it anymore. Democritus called these chunks atoms ("no division").
In the fourth century BC., Empedocles postulated that matter was composed of 4 elements: earth, air, water and fire.
Aristotle then postulated that matter was composed of these 4 elements but denies the idea of atom, a fact that was maintained until 200 years later in the thinking of mankind.
In 1808, John Dalton published his atomic theory, which incorporated the old ideas of Leucippus and Democritus. Dalton's theory:
1. The elements are composed of tiny particles called atoms indivisible and unchanging.
Dalton established a system to designate each atom so that it could distinguish between the different elements:
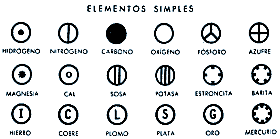
2. Atoms of an element are all equal to each other in mass, size and on the other physical or chemical properties. By contrast, the atoms of different elements have different mass and properties.
3. The compounds are formed by the union of corresponding elements atoms as a simple numerical ratio constant.
Thomson's atomic model
For such a small mass of electrons, the English physicist J. J. Thomson assumed in 1904 that most of the mass of the atom corresponding to the positive charge, which therefore should occupy most of the atomic volume. Thomson imagined the atom as a kind of continuous positive field in which electrons are embedded (like raisins in a pudding).

Rutherford's atomic model
Thomson's model was widely accepted until in 1911 the English chemist and physicist Ernest Rutherford and his colleagues carried out the "Rutherford Experiment".
In the experiment, bombarded a thin gold foil with alpha particles (positive) from a radioactive material and noted that:
- Most of the alpha particles passed through the film without changing direction, as expected.
- Some alpha particles deviate considerably.
- A few alpha particles rebounded to the emission source
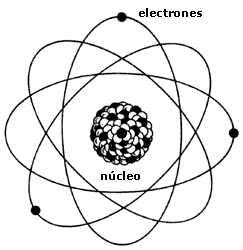
Accordingly, the atom was composed as follows:
- A central zone or core where the total charge is positive (the protons) and most of the mass of the atom, provided by the protons and neutrons.
- An outer zone or cortex where are the electrons orbiting the nucleus.
There are the same electrons in the cortex that protons in the core, so that the whole is electrically neutral atom.
Bohr's atomic model
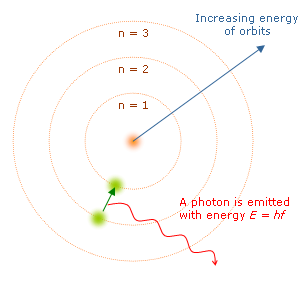 To solve these problems, the Danish physicist Niels Bohr formulated in 1913, a hypothesis about the atomic structure. His assumptions were:
To solve these problems, the Danish physicist Niels Bohr formulated in 1913, a hypothesis about the atomic structure. His assumptions were:1) The electron only moves in a circular orbits "allowed" (stable) under which does not emit energy. The electron has a certain energy per orbit, which is greater the more remote the orbit the nucleus.
2) The power output occurs when an electron jumps from an initial state of higher energy to a lower energy.
It's really amazing how man has come to discover the atom and so to determine that matter is made of.
ResponderEliminar