| |||
miércoles, 29 de agosto de 2012
jueves, 23 de agosto de 2012
Albert Einstein
 Albert Einstein definitely was and is the greatest scientist in history.
Albert Einstein definitely was and is the greatest scientist in history.Born in the Bavarian city of Ulm on March 14, 1879. He was the eldest son of Hermann Einstein and Pauline Koch, both Jews whose families came from Swabia. The following year they moved to Munich, where his father was established, along with his brother Jakob, as a trader in the developments of the era electro.
Little Albert was a child still and pensive, which had a slow intellectual development. Einstein himself attributed to the fact that slowly have been the only person to develop a theory of relativity as "a normal adult is not concerned about the problems posed by space and time, believing that everything to know what is already known about since early childhood. I, on the contrary, I have had a development so slow that I have begun to wonder questions about space and time until I was old. "
In 1894, the economic difficulties that the family did (increased since 1881, on the birth of a daughter, Maya) moved to Milan, Einstein stayed in Munich to finish high school, meeting with parents the following year. In the fall of 1896, he began his studies at the Technische Hochschule in Zurich Eidgenossische, where he was a pupil of the mathematician Hermann Minkowski, who later generalized four-dimensional formalism introduced by the theories of his former pupil. The June 23, 1902, began to provide services in the Office of Intellectual Property Confederal Berne, where he worked until 1909. In 1903, he married Mileva Maric, a former fellow student in Zurich, with whom he had two sons, Hans Albert and Eduard, born respectively in 1904 and 1910. In 1919 they divorced and remarried Einstein with his cousin Elsa.
During 1905, five papers published in the Annalen der Physik, the first of them earned a doctoral degree from the University of Zurich, and the remaining four eventually impose a radical change in the image that science offers the universe. Of these, the first providing a theoretical explanation, statistically, Brownian motion and the second gave a photoelectric effect interpretation based on the assumption that light is composed of individual quanta, later called photons, the two remaining work laid the foundations of the theory of relativity, establishing the equivalence between the energy E of a certain quantity of matter and its mass m, in terms of the famous equation E = mc ², where c is the speed of light, which assumed constant.
Einstein's effort placed him immediately among the most eminent physicists of Europe, but the public recognition of the true extent of his theories came quickly, the Nobel Prize in Physics, which was awarded in 1921 it was only "for his work on Brownian motion and its interpretation of the photoelectric effect ". In 1909, he began his career as a university lecturer in Zurich, then going back to Prague and back to Zurich in 1912 to become a professor at the Polytechnic, where he had studied. In 1914 he went to Berlin as a member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences. The outbreak of the First World War forced him to leave his family, then vacation in Switzerland and no longer meet him again.
Against the general feeling of the academic community in Berlin, Einstein then manifested openly antiwar attitudes influenced by the doctrines pacifist Romain Rolland. In scientific terms, its business focused, between 1914 and 1916, in the improvement of the general theory of relativity, based on the assumption that gravity is not a force but a field created by the presence of a mass in the space-time continuum. The confirmation of his predictions came in 1919, to photograph the solar eclipse of May 29, The Times introduced him as the new Newton and his international fame grew, forcing you to multiply your outreach conferences worldwide and popularizing his image Traveler the third class rail, with a violin case under his arm.
Over the next decade, Einstein concentrated on finding a mathematical relationship between electromagnetism and gravitational attraction, determined to move towards that, for him, should be the ultimate goal of physics: discover the common laws that supposedly had govern the behavior of all objects in the universe, from subatomic particles to the stellar bodies. Such research, he held the rest of his life, and eventually unsuccessful acarrearle estrangement from the rest of the scientific community.
Since 1933, with Hitler's accession to power, his loneliness was compounded by the need to renounce his German citizenship and move to the U.S., where he spent the last twenty years of his life at the Institute of Advanced Studies Princeton, the city where he died on April 18, 1955.
Einstein once said that politics had a passenger value, while a value equation for eternity. In the last years of his life, the bitterness over not find the formula to reveal the secret of the unity of the world had to accentuate the need that was felt dramatically intervene in the political sphere. In 1939, urged by physicists Leo Szilard and Wigner Paul, and convinced of the possibility that the Germans were able to build an atomic bomb, addressed to President Roosevelt urging him to undertake a program of research on atomic energy.
After the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, joined scientists seeking ways to prevent future use of the pump and proposed the formation of a world government from the embryo formed by the United Nations. But his proposals towards mankind avoid destruction threats individually and collectively, made on behalf of a singular amalgam of science, religion and socialism, the politicians received a rejection comparable to criticism respectful scientists raised among successive versions of the idea of a unified field.
http://www.biografiasyvidas.com/monografia/einstein/
To my Einstein was and will be one of the greatest scientists in history, what do you think?, The scientist who was most important to you?
jueves, 2 de agosto de 2012
The atom and its evolution over the course of history:
In the V century. BC, Leuccipus said there was only one type of matter and thought that if we divided the matter into ever smaller parts, we get a piece that could not cut it anymore. Democritus called these chunks atoms ("no division").
In the fourth century BC., Empedocles postulated that matter was composed of 4 elements: earth, air, water and fire.
Aristotle then postulated that matter was composed of these 4 elements but denies the idea of atom, a fact that was maintained until 200 years later in the thinking of mankind.
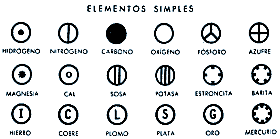
In 1808, John Dalton published his atomic theory, which incorporated the old ideas of Leucippus and Democritus. Dalton's theory:
1. The elements are composed of tiny particles called atoms indivisible and unchanging.
Dalton established a system to designate each atom so that it could distinguish between the different elements:
2. Atoms of an element are all equal to each other in mass, size and on the other physical or chemical properties. By contrast, the atoms of different elements have different mass and properties.
3. The compounds are formed by the union of corresponding elements atoms as a simple numerical ratio constant.
Thomson's atomic model
For such a small mass of electrons, the English physicist J. J. Thomson assumed in 1904 that most of the mass of the atom corresponding to the positive charge, which therefore should occupy most of the atomic volume. Thomson imagined the atom as a kind of continuous positive field in which electrons are embedded (like raisins in a pudding).

Rutherford's atomic model
Thomson's model was widely accepted until in 1911 the English chemist and physicist Ernest Rutherford and his colleagues carried out the "Rutherford Experiment".
In the experiment, bombarded a thin gold foil with alpha particles (positive) from a radioactive material and noted that:
- Most of the alpha particles passed through the film without changing direction, as expected.
- Some alpha particles deviate considerably.
- A few alpha particles rebounded to the emission source
Accordingly, the atom was composed as follows:
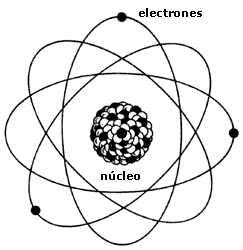
- A central zone or core where the total charge is positive (the protons) and most of the mass of the atom, provided by the protons and neutrons.
- An outer zone or cortex where are the electrons orbiting the nucleus.
There are the same electrons in the cortex that protons in the core, so that the whole is electrically neutral atom.
Bohr's atomic model
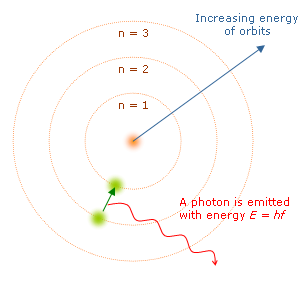 To solve these problems, the Danish physicist Niels Bohr formulated in 1913, a hypothesis about the atomic structure. His assumptions were:
To solve these problems, the Danish physicist Niels Bohr formulated in 1913, a hypothesis about the atomic structure. His assumptions were:1) The electron only moves in a circular orbits "allowed" (stable) under which does not emit energy. The electron has a certain energy per orbit, which is greater the more remote the orbit the nucleus.
2) The power output occurs when an electron jumps from an initial state of higher energy to a lower energy.
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)